SP-009-002 Contracts
No one should ever access our product without having signed a contract first. Not even for demonstration purposes.
What will you learn here?
- Why contracts are
importantmandatory - What type of contracts we sign with clients
- Where can you find the templates
- How to create and use templates
- What steps you should follow in the contracting stage
Steps to follow in the contracting stage
Generally speaking, this is the ideal course of action:
- Ask the client for the necessary information
- Create a contract from a template inside the client's folder in our Drive
- Add the client's information to the contract
- Consider what changes are necessary for the contract to match the deal's requirements
- Send the contract to the client for them to review internally
- If everything is agreed upon, send the client a PDF export for them to sign
- Receive back the signed contract, and send it to our CEO so she can sign it
- Send it to the client via email
- Save the signed PDF inside the client's folder in our Drive
In order for a contract to be valid, it must include the following information:
- About the company that signs the contract
- Name of the company (as it is legally incorporated)
- VAT number or the applicable govermental ID number of the company
- Full address of the company
- About the individual person representing the company
- Position of the individual that makes them a legally authorised representative
- Full name (first, and last name)
- Govermental ID number of the individual, such as DNI or passport number
Types of contract
The contract we sign with clients depends on what they are buying. The things that clients may end up buying can be classified as follows, from a contractual standpoint:
And for each of them, we use a template
| Thing | Template |
|---|---|
| Access to our device | 📄 License of Use and Order Sheet |
| Custom developments | 📄 Service provision contract |
| Something else | 🤷 |
Unfortunatelly, in many occasions the specifics of the deal or the objections of the client may force us to make changes to our contracts, or even use their templates, which may not look at all like our models. This complicates everything, so try to avoid it.
Things that contracts regulate
Here's a list of the main things that contracts define in our relationship with the client.
- Privacy clauses under GDPR
- Payment method and prices
- Confidentiality
- Responsabilities of each party
- Intellectual property
Keep in mind that our contracts can not force our customers to do anything. Their patients are their business. The only thing we can do if provide adequate instructions and be clear about things.
License of Use and Order Sheet
Frequently asked questions
- Where can I find the template?
- In our template gallery
- What type of document is it?
- Google Sheets document
- Does it have mandatory annexes?
- Yes, the Order Sheet is mandatory
- Does it have optional annexes?
- Yes, such as the Addendum
How to use
Here's the course of action
- Inside the
Variables for Contracttab, add the information of the client. - Make sure that the
Contracttab is being filled in correctly from the variables - Inside the
Variables for Order Sheettab, add the information about the deal. Here you will specify things such as how we are pricing the product (by patients or diagnostic reports) or is we charge for additional services (such as integration or setup). - Make sure that the
Order sheettab is being filled in correctly from the variables
In the following image you will see how the template looks like. At the bottom, you can see the tabs Variables for Contract and Variables for Order Sheet.
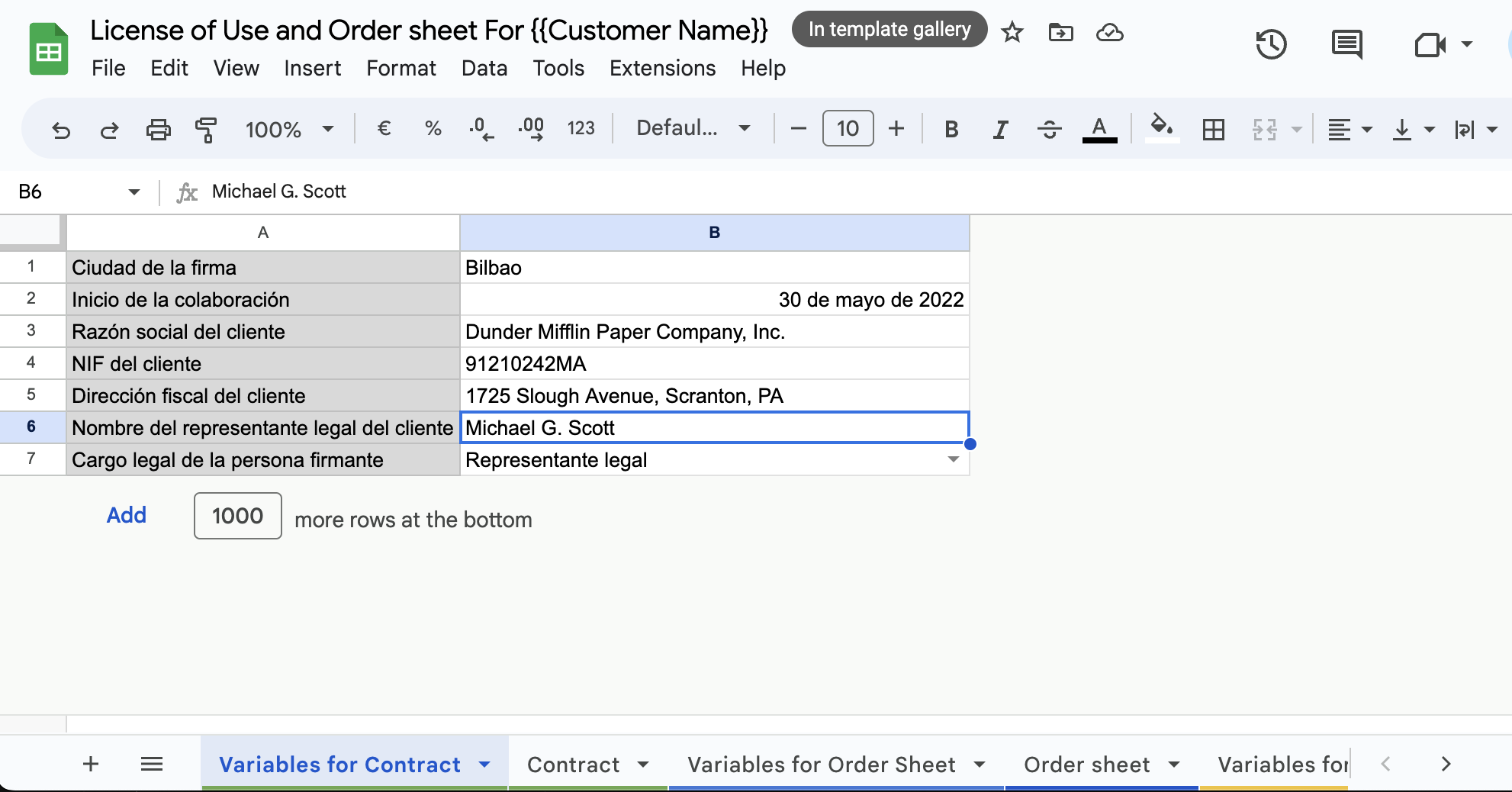
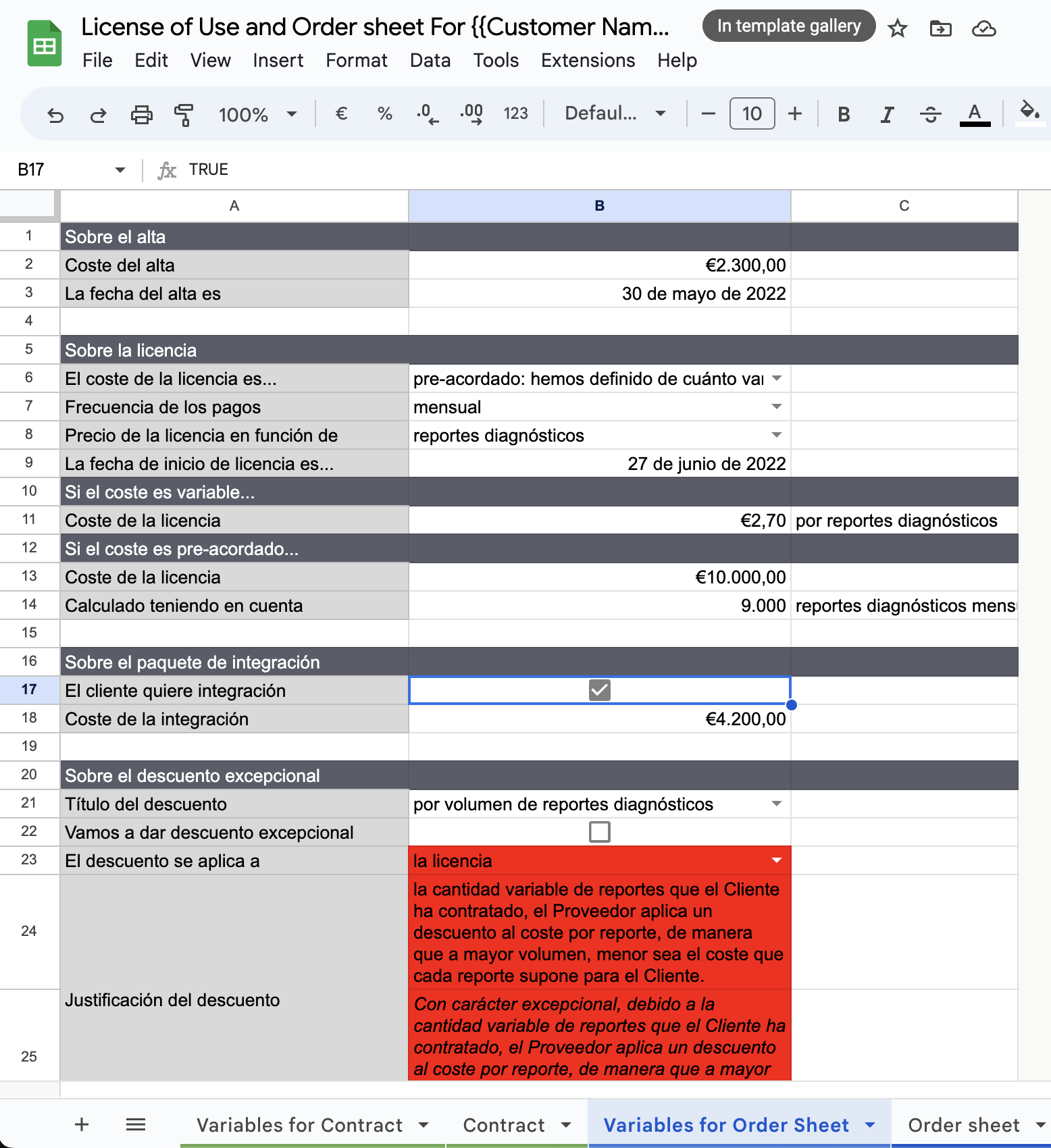
The tab for Variables for Order Sheet is the most complex. You should pay close attention to every field, because there is useful knowledge embeded there:
There are two types of tab in the template
- Variables
- Content
The variables tabs are only for internal use. When you fill-in the variables, the other tabs are populated with this information. This is for your convenience and to avoid manual error, and you should not send this to the client.
Service provision contract
As of today, we don't have a template.
How to use
Ask your manager which past deals are similar to the deal you are facing, and use that as a template. Then, simply follow the basic steps set out at the begining of this article.
Why are contracts so important?
If this is not clear for you, it means that you are lacking some very important knowledge.
There are so many reasons why contracts are importante that is it pointless to try to explain it here. For now, just be aware that there is a worrying gap in your knowledge and you should take steps to remediate it.
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to describe how we use contracts with customers.
Scope
This document applies to the contracts we use during the sales process of all our medical devices, which are software devices.
Responsibilities
Same as the parent procedure, GP-009 Sales.
Associated documents
GP-009 Sales
Signature meaning
The signatures for the approval process of this document can be found in the verified commits at the repository for the QMS. As a reference, the team members who are expected to participate in this document and their roles in the approval process, as defined in Annex I Responsibility Matrix of the GP-001, are:
- Author: Team members involved
- Reviewer: JD-003 Design & Development Manager, JD-004 Quality Manager & PRRC
- Approver: JD-001 General Manager