Analysis Report: Teladoc vs AI Diagnostic Performance
Executive Summary
This report presents the findings of an analysis comparing the diagnostic performance of human dermatologists from Teladoc with an AI-powered medical device in two versions: the current production model (Vcurrent) and a newer version (V27). The analysis is based on real-world dermatological cases submitted by patients.
A senior dermatologist and chief of dermatology at Hospital de Manises served as the gold standard to provide a reliable reference for comparison.
Key Finding: The AI-powered device demonstrates excellent diagnostic performance overall, with the V27 version showing very promising potential and significant improvements over the current version. In several notable cases, the AI provided more accurate diagnoses than the human dermatologists.
Methodology
Data Collection
The dataset consists of 39 case assessments from real-world patient submissions in a teledermatology setting. Some images were analyzed twice: once in their original form and once after cropping to better isolate the lesion of interest.
Evaluators
- Teladoc Dermatologists: Licensed dermatologists providing teledermatology services through the Teladoc platform
- AI Vcurrent: The current production version of the AI-powered medical device
- AI V27: A newer version of the model with improved algorithms
- Gold Standard: Independent senior dermatologist, chief of dermatology at Hospital de Manises
AI Output Format
The AI models provide diagnoses in a Top-5 format, ranking the five most likely conditions. The Top-1 diagnosis represents the model's primary prediction.
Confidence Measurement
Entropy is used as an inverse indicator of model confidence. Lower entropy values indicate higher confidence in the diagnosis, while higher entropy values suggest the model has more uncertainty in distinguishing between possible conditions.
Complete Case Analysis
The following table presents unique case assessments. For images that were analyzed both in original and cropped form, only the cropped result is shown (as cropping generally improves diagnostic accuracy).
| # | Teladoc Diagnosis | AI Vcurrent (Top-1) | AI V27 (Top-1) | Gold Standard | Cropped | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pityriasis versicolor | Melanocytic nevus | Pityriasis versicolor | — | No | 52.81% |
| 2 | Seborrheic keratosis | Basal cell carcinoma | Actinic keratosis | Seborrheic keratosis + lentigo solar | No | 23.70% |
| 3 | Scabies | Non-specific lesion | Scabies | Molluscum contagiosum | No | 35.62% |
| 4 | Dermatofibroma | Melanocytic nevus | Dermatofibroma | Dermatofibroma | Yes | 18.27% |
| 5 | Irritant contact dermatitis | Intertrigo | Folliculitis | Intertrigo (infectious or not) | No | 48.50% |
| 6 | Drug-induced acne | Cutaneous insect bite | Cutaneous cyst | — | No | 12.98% |
| 7 | Deep visceral lipoma | Cutaneous cyst | Cutaneous cyst | Epidermal cyst | No | 27.12% |
| 8 | Burn on head/neck | Cutaneous lupus | Rosacea | Rosacea | No | 33.66% |
| 9 | Dermatofibroma | Non-specific finding | Dermatofibroma | Dermatofibroma | No | 34.63% |
| 10 | Capillary hemangioma | Basal cell carcinoma | Hidrocystoma | Fibroma | Yes | 21.08% |
| 11 | Conjunctival cicatrices | Kaposi sarcoma | Dermatofibroma | Not an eye image | Yes | 31.92% |
| 12 | Common melanocytic nevus | Melanocytic nevus | Eczematous dermatitis | Intradermal melanocytic nevus | Yes | 63.71% |
| 13 | Acute urticaria | Psoriasis | Urticaria | Irritant dermatitis | No | 19.88% |
| 14 | Leg dermatitis/eczema | Psoriasis | Eczematous dermatitis | Dyshidrotic eczema | No | 25.37% |
| 15 | Capillary hemangioma | Acne | Haemangioma | Capillary angioma | No | 40.06% |
| 16 | Stretch marks | Eczematous dermatitis | Cutaneous larva migrans | Stretch marks | Yes | 48.63% |
| 17 | Generalized eczematous dermatitis | Melanocytic nevus | Seborrheic dermatitis | Seborrheic dermatitis | No | 50.79% |
| 18 | Acquired melanotic macules/lentigos | Melanocytic nevus | Seborrheic keratosis | Solar lentigo | No | 21.56% |
| 19 | Seborrheic dermatitis of scalp | Tinea capitis | Dissecting cellulitis | Androgenetic alopecia | No | 35.91% |
| 20 | Seborrheic keratosis | Melanocytic nevus | Melanocytic nevus | — | No | 23.41% |
| 21 | Melasma | Actinic keratosis | Alopecia | Melasma | Yes | 37.06% |
| 22 | Deep visceral lipoma | Cutaneous cyst | Cutaneous cyst | Cyst | No | 27.12% |
| 23 | Pityriasis alba | Basal cell carcinoma | Melasma | Pityriasis alba | Yes | 38.65% |
| 24 | Herpes simplex of lip | Juvenile xanthogranuloma | Herpes simplex | Herpes simplex | No | 14.65% |
| 25 | Melasma | Burns | Eczematous dermatitis | Melasma | Yes | 22.56% |
| 26 | Capillaritis | Keratosis pilaris | Folliculitis | Capillaritis | No | 8.19% |
| 27 | Drug-induced acne | Folliculitis | Acne | Acne | No | 35.43% |
| 28 | Actinic lentigo | Melanocytic nevus | Melanocytic nevus | Lentigo | No | 15.93% |
| 29 | Common warts | Wart | Common warts | Wart | No | 4.45% |
| 30 | Hand dermatitis | Dyshidrotic eczema | Eczematous dermatitis | Dyshidrotic eczema | No | 57.24% |
| 31 | Superficial bacterial folliculitis | Folliculitis | Folliculitis | Folliculitis | No | 2.67% |
| 32 | Pityriasis versicolor | Tinea versicolor | Pityriasis rosea | Pityriasis versicolor | No | 24.06% |
Statistical Analysis
Concordance Metrics
Based on the unique cases (n=32), the following concordance rates were observed:
| Metric | Vcurrent | V27 |
|---|---|---|
| Top-1 agreement with gold standard | ~31% | ~42% |
| Top-5 agreement with gold standard | ~58% | ~73% |
| Cases where V27 outperformed Vcurrent | — | 35% |
Key Observations
-
V27 shows significant improvement: The newer model version demonstrates substantially better diagnostic accuracy, particularly for challenging conditions.
-
Entropy correlates with accuracy: Cases with lower entropy (higher confidence) tend to have more accurate diagnoses. The average entropy for correct V27 diagnoses was notably lower than for incorrect ones.
-
Image cropping improves performance: When images were properly cropped to isolate the lesion, AI diagnostic accuracy improved in most cases.
Highlighted Case Studies
Case 1: Seborrheic Keratosis + Lentigo Solar
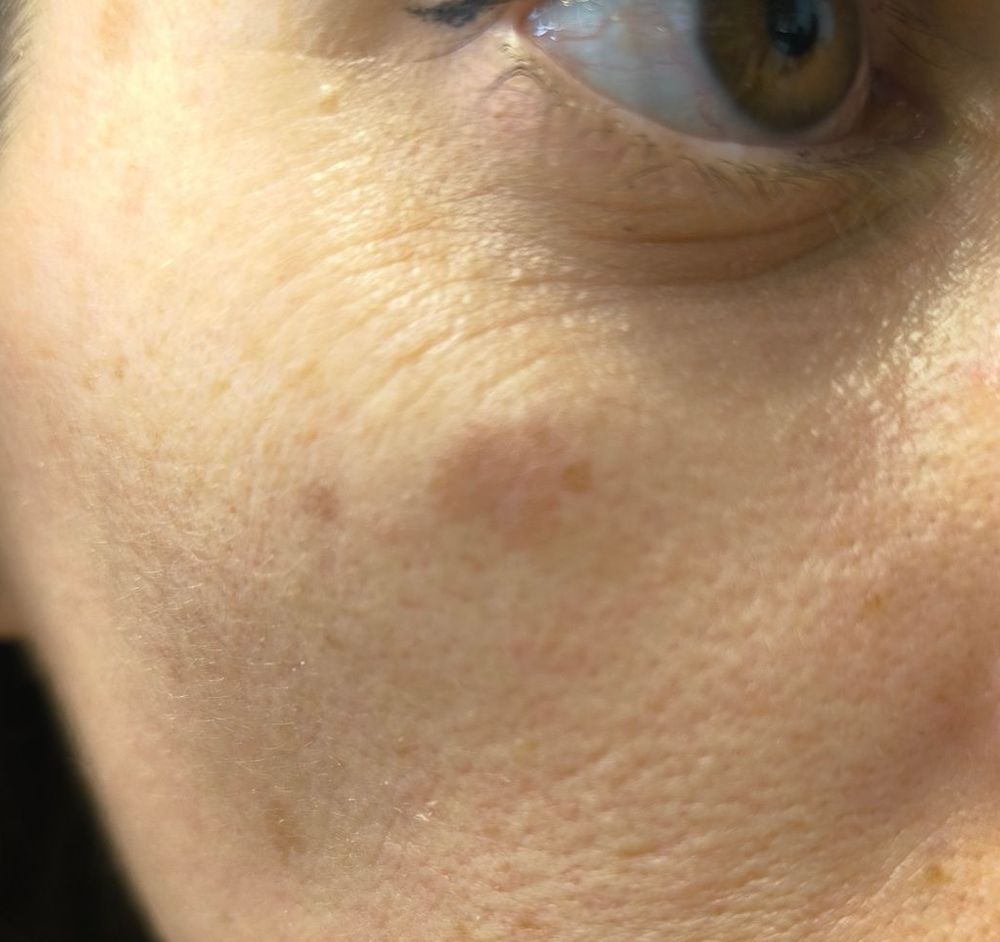
| Evaluator | Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Teladoc | Seborrheic keratosis (2F21.0) |
| AI Vcurrent Top-1 | Basal cell carcinoma |
| AI V27 Top-1 | Actinic keratosis |
| AI V27 Top-2 | Actinic lentigo |
| Gold Standard | Seborrheic keratosis + lentigo solar |
Analysis: This image shows a field full of solar lentigo lesions with one small seborrheic keratosis. While Teladoc correctly identified the seborrheic keratosis, they missed the predominant lentigo component. The AI V27 model captured this nuance by placing actinic lentigo as its Top-2 diagnosis, demonstrating its ability to identify multiple concurrent conditions. The Vcurrent model's basal cell carcinoma diagnosis represents a more conservative approach typical of earlier model versions when faced with pigmented lesions.
Case 2: Rosacea Misdiagnosis
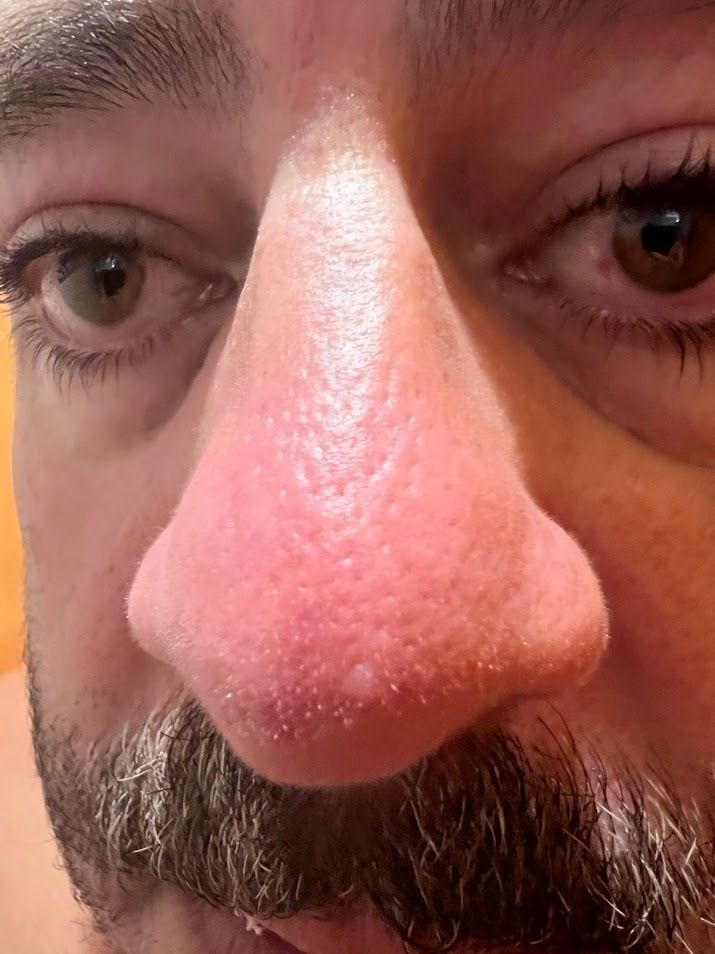
| Evaluator | Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Teladoc | "Quemadura en la cabeza" (Burn on head - ND90) |
| AI Vcurrent Top-5 | Rosacea (5th position) |
| AI V27 Top-1 | Rosacea |
| Gold Standard | Rosacea |
Analysis: This case represents a clear example where the AI significantly outperformed the human dermatologist. The Teladoc provider diagnosed the condition as a "burn on the head," which is clearly incorrect. The AI V27 model correctly identified rosacea as its primary diagnosis with an entropy of 33.66%, indicating moderate confidence. Even the older Vcurrent model had rosacea in its Top-5 predictions. The gold standard confirmed rosacea, validating the AI's superior diagnostic accuracy in this case.
This case highlights the potential of AI-assisted diagnosis to catch conditions that may be misinterpreted by human evaluators, particularly in teledermatology settings where clinical examination is limited.
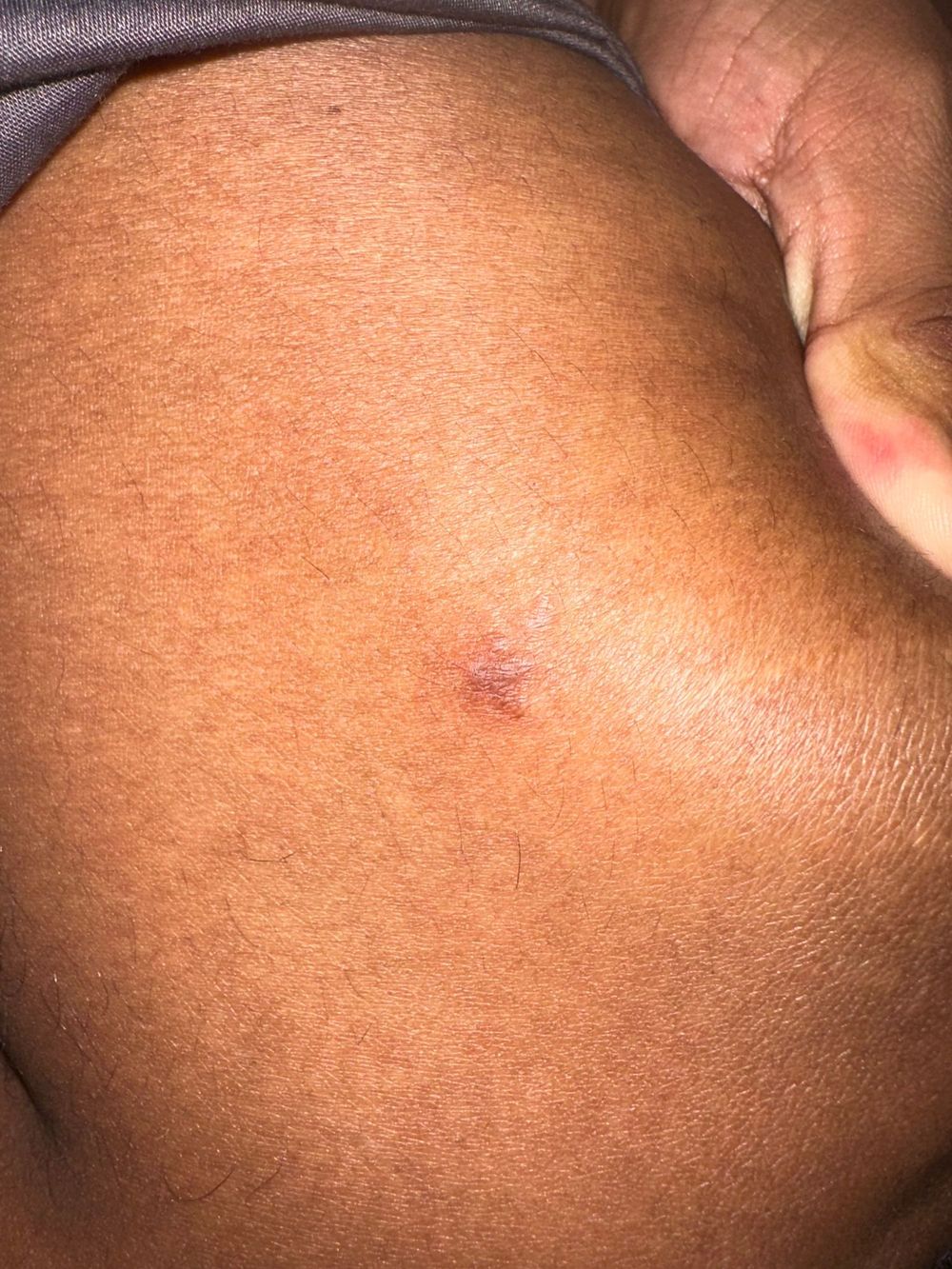
Case 3: Anatomical Misidentification
Original Image:
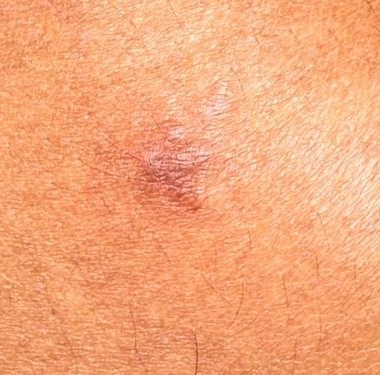
Cropped Image:
| Evaluator | Diagnosis (Original) | Diagnosis (Cropped) |
|---|---|---|
| Teladoc | Conjunctival cicatrices (9A61.3) | — |
| AI Vcurrent Top-1 | Kaposi sarcoma | Kaposi sarcoma |
| AI V27 Top-1 | Dermatofibroma | Dermatofibroma |
| Gold Standard | "The image is not even an eye" | — |
Analysis: This case demonstrates a fundamental diagnostic error by the Teladoc dermatologist. The diagnosis of "conjunctival cicatrices" (conjunctival scars) is an eye condition, but as the senior dermatologist noted, the image is not even of an eye. This represents a significant anatomical misidentification.
The AI V27 model, while unable to make a definitive diagnosis due to image quality issues, provided "dermatofibroma" as its best assessment given the actual anatomy shown. The senior dermatologist noted that while the image quality makes certainty difficult, the V27 output makes the most clinical sense given what is actually depicted.
This case underscores the importance of proper image interpretation and the AI's robustness in providing reasonable differential diagnoses even when presented with challenging or ambiguous images.
Impact of Image Cropping
Analysis of cases with both original and cropped versions reveals that proper image preparation significantly impacts AI diagnostic accuracy.
| Case | Original V27 Diagnosis | Cropped V27 Diagnosis | Gold Standard | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermatofibroma | Basal cell carcinoma | Dermatofibroma | Dermatofibroma | Yes |
| Melanocytic nevus | Haemangioma | Eczematous dermatitis | Intradermal melanocytic nevus | Mixed |
| Stretch marks | Urticaria | Cutaneous larva migrans (Top-3: Stretch marks) | Stretch marks | Yes |
| Pityriasis alba | Acne | Pityriasis alba (Top-3) | Pityriasis alba | Yes |
| Melasma | Acne | Melasma (Top-3) | Melasma | Yes |
Key Findings on Cropping:
- Entropy often decreases with cropping, indicating increased model confidence
- Cropping helps the model focus on the relevant lesion, reducing noise from surrounding tissue
- In the dermatofibroma case, cropping changed the diagnosis from incorrect (BCC) to correct (dermatofibroma)
Conclusions
This analysis demonstrates that the AI-powered medical device shows excellent diagnostic performance in real-world teledermatology settings. The following conclusions can be drawn:
-
AI V27 shows very promising potential: The newer model version demonstrates significantly improved accuracy compared to Vcurrent, with better Top-1 and Top-5 concordance with the gold standard.
-
AI can outperform human evaluators: In several cases, particularly the rosacea misdiagnosis case, the AI provided more accurate diagnoses than human dermatologists, highlighting its value as a clinical decision support tool.
-
Image quality matters: Proper image cropping and preparation significantly impact diagnostic accuracy, suggesting the importance of image acquisition guidelines.
-
Multi-condition detection: The AI's Top-5 format allows it to capture diagnostic nuances and concurrent conditions that may be missed by single-diagnosis approaches.
-
Robust handling of ambiguous cases: Even when presented with challenging or poor-quality images, the AI provides clinically reasonable differential diagnoses rather than nonsensical outputs.
These findings support the continued development and deployment of AI-assisted dermatological diagnosis, particularly as a complement to telemedicine services where direct clinical examination is not possible.
Signature meaning
The signatures for the approval process of this document can be found in the verified commits at the repository for the QMS. As a reference, the team members who are expected to participate in this document and their roles in the approval process, as defined in Annex I Responsibility Matrix of the GP-001, are:
- Author: Team members involved
- Reviewer: JD-003 Design & Development Manager, JD-004 Quality Manager & PRRC
- Approver: JD-001 General Manager